Jonghyun Ho
OpenAI gym Cartpole
CartPole 이라는 환경에서 강화 학습 기법을 이용하여 주어진 목적을 달성해내는 과정을 시험해보고자 한다.
강화학습
강화 학습(Reinforcement learning)은 기계 학습의 한 영역이다. 어떠한 환경에서 소프트웨어 에이전트가 현재의 상태를 인식하여 특정 행동을 수행했을 때 환경으로부터 보상을 받을 수 있다. 이 누적된 보상의 값을 최대화하기 위해 최선의 행동들을 선택하여 목적을 달성할 수 있도록 하는 학습 방법이다.
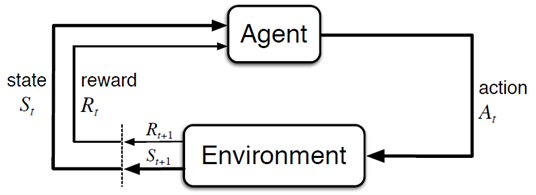
- 참고 : 강화학습
Cartpole
OpenAI gym의 CartPole은 카트 위에 막대기가 고정되어 있고 막대기는 중력에 의해 바닥을 향해 자연적으로 기울게 되는 환경을 제공한다. CartPole 의 목적은 카트를 좌, 우로 움직이며 막대기가 기울지 않고 서 있을 수 있도록 유지시켜 주는 것이 목적인데, 강화 학습 알고리즘을 이용하여 막대기를 세울 수 있는 방법을 소프트웨어 에이전트가 스스로 학습할 수 있도록 한다.
아래는 CartPole 환경을 생성하여 episode 를 반복하는 예제이다.
import gym
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
for i_episode in range(20):
observation = env.reset()
for t in range(100):
env.render()
print(observation)
action = env.action_space.sample()
observation, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
if done:
print("Episode finished after {} timesteps".format(t+1))
break
env.close()
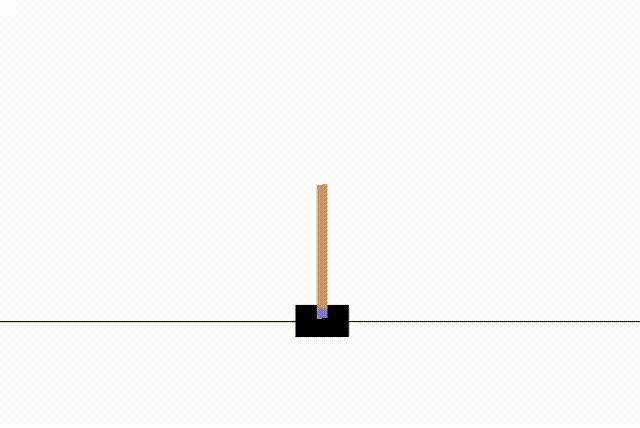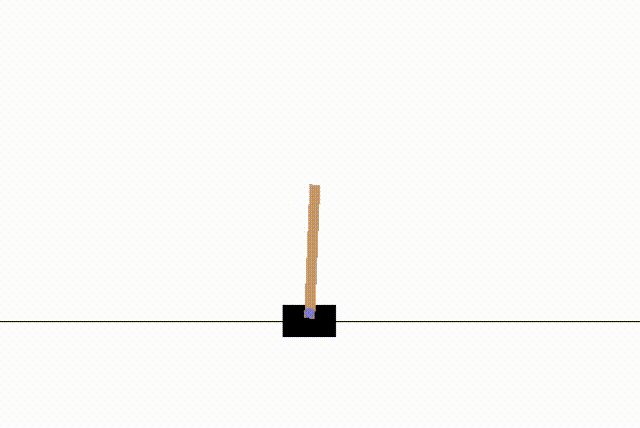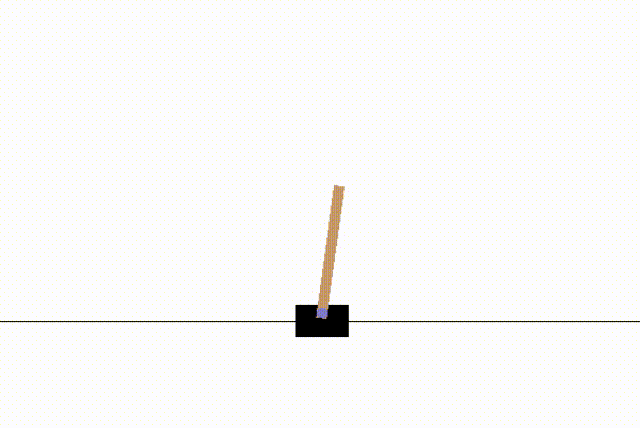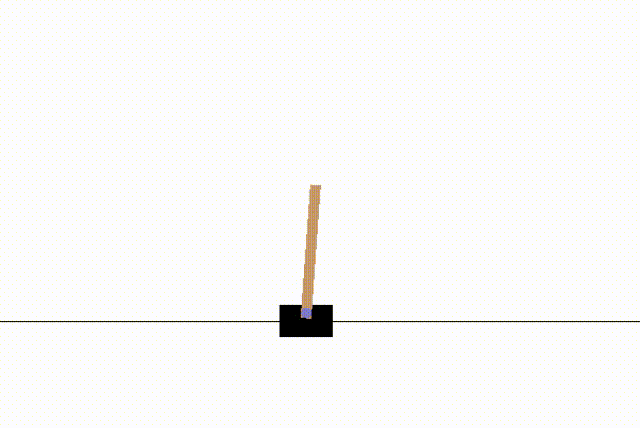
env.action_space.sample()을 호출하면 좌, 우의 값이 0과 1로 랜덤하게 전달된다.
env.step(action)을 통해 랜덤한 움직임에 대한 action을 한번 수행하고, action이 실행된 이후의 상태(observation)와, 보상(reward), 막대가 쓰러졌는지의 여부(done) 등의 정보가 반환된다.
다음은 CartPole 환경에서 사용되는 observation, action, reward 의 값과 episode의 시작과 종료에 대한 설명이다.
Observation:
Type: Box(4)
Num Observation Min Max
0 Cart Position -4.8 4.8
1 Cart Velocity -Inf Inf
2 Pole Angle -24 deg 24 deg
3 Pole Velocity At Tip -Inf Inf
Actions:
Type: Discrete(2)
Num Action
0 Push cart to the left
1 Push cart to the right
Reward:
Reward is 1 for every step taken, including the termination step
Starting State:
All observations are assigned a uniform random value in [-0.05..0.05]
Episode Termination:
Pole Angle is more than 12 degrees.
Cart Position is more than 2.4 (center of the cart reaches the edge of
the display).
Episode length is greater than 200.
Solved Requirements:
Considered solved when the average reward is greater than or equal to
195.0 over 100 consecutive trials.
DQN 알고리즘
DQN 알고리즘의 pseudo code 는 다음과 같다.

Cartpole DQN 강화 학습
학습을 위한 tensorflow를 포함하여 필요한 모듈을 임포트 한다.
import gym
import sys
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import deque
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras.initializers import RandomUniform
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
상태가 입력, Q 함수가 출력인 인공신경망 생성
class DQN(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, action_size):
super(DQN, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = Dense(24, activation='relu')
self.fc2 = Dense(24, activation='relu')
self.fc_out = Dense(action_size, kernel_initializer=RandomUniform(-1e-3, 1e-3))
def call(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
q = self.fc_out(x)
return q
CartPole 환경에서 agent 역할을 하는 DQNAgent 클래스이다. CartPole 환경에서는 4가지의 상태와 2가지의 행동으로 이루어진다.
class DQNAgent:
def __init__(self, state_size, action_size):
self.state_size = state_size
self.action_size = action_size
DQN 알고리즘을 구동하기 위한 하이퍼파라미터 값을 설정한다.
self.discount_factor = 0.99
self.learning_rate = 0.001
self.epsilon = 1.0
self.epsilon_decay = 0.999
self.epsilon_min = 0.01
self.batch_size = 64
self.train_start = 1000
리플레이 메모리는 최대 크기 2000 으로 설정하였다.
self.memory = deque(maxlen=2000)
model 과 target_model 두 개의 인공신경망을 생성한다. Q 함수를 학습하기 위해 model의 파라미터가 학습 도중 갱신되는데, 이 파라미터의 변경으로 인하여 정답으로 간주되는 다음 상태의 Q 함수도 함께 변경이 된다. 이를 막기 위해 다음 상태의 Q 함수를 위한 별도의 target_model을 분리하여 사용한다.
self.model = DQN(action_size)
self.target_model = DQN(action_size)
self.optimizer = Adam(lr=self.learning_rate)
self.update_target_model()
update_target_model은 target_model의 가중치를 model의 가중치로 업데이트 하는 함수이다. 일정 주기로 타겟 흔들림을 해결하기 위해 분리된 model 과 target_model 네트워크의 가중치를 일치시킨다.
def update_target_model(self):
self.target_model.set_weights(self.model.get_weights())
리플레이 메모리에 현재 상태 S, 액션 A, 보상 R, 다음 상태 S’, 완료 여부 done 을 저장한다.
def remember(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.memory.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
epsilon을 이용하여 탐험(Exploration)과 활용(Exploitation)의 비율을 조정한다.
학습된 정보만을 이용하여 action 을 선택하게 되면 새로운 환경에 대해 경험해 볼 수 없기 때문에 랜덤한 수를 골라 e 보다 작으면 랜덤, 그렇지 않으면 학습된 모델을 사용하는 E-greedy 정책을 사용한다.
def choose_action(self, state):
return random.randrange(self.action_size) if (np.random.rand() <= self.epsilon) else np.argmax(self.model.predict(state))
샘플 간 correlation 을 줄이기 위해 리플레이 메모리에 저장된 데이터를 랜덤하게 섞어 훈련에 사용할 미니 배치 데이터를 생성한다.
벨만 최적 방정식을 이용하여 계산된 정답에 해당하는 targets 와 예상 값 predicts 의 차이를 줄여 나가는 경사 하강법으로 학습을 진행한다.
def train_model(self):
if self.epsilon > self.epsilon_min:
self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decay
mini_batch = random.sample(self.memory, self.batch_size)
states = np.array([sample[0][0] for sample in mini_batch])
actions = np.array([sample[1] for sample in mini_batch])
rewards = np.array([sample[2] for sample in mini_batch])
next_states = np.array([sample[3][0] for sample in mini_batch])
dones = np.array([sample[4] for sample in mini_batch])
model_params = self.model.trainable_variables
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
predicts = self.model(states)
one_hot_action = tf.one_hot(actions, self.action_size)
predicts = tf.reduce_sum(one_hot_action * predicts, axis=1)
target_predicts = self.target_model(next_states)
target_predicts = tf.stop_gradient(target_predicts)
max_q = np.amax(target_predicts, axis=-1)
targets = rewards + (1 - dones) * self.discount_factor * max_q
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(targets - predicts))
grads = tape.gradient(loss, model_params)
self.optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model_params))
CartPole-v1 환경과 그 환경에서 학습을 진행하게 될 DQNAgent를 생성한다.
if __name__ == "__main__":
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
state_size = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_size = env.action_space.n
agent = DQNAgent(state_size, action_size)
scores, episodes = [], []
score_avg = 0
episode 가 시작될 때마다 환경을 초기화한다.
num_episode = 300
for e in range(num_episode):
done = False
score = 0
state = env.reset()
state = state.reshape(1, -1)
현재 상태에서 action 을 하나 선택하여 한 스텝 진행한다.
그 결과로 받은 보상을 현재 상태와 선택한 행동과 함께 리플레이 메모리에 저장한다.
리플레이 메모리가 일정 크기 이상으로 저장되면 매 스텝마다 학습할 수 있도록 한다.
while not done:
env.render()
action = agent.choose_action(state)
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
next_state = next_state.reshape(1, -1)
score += reward
reward = 0.1 if not done or score == 500 else -1
agent.remember(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
if len(agent.memory) >= agent.train_start:
agent.train_model()
state = next_state
한 episode 가 완료될 때마다 target_model 을 model의 가중치와 일치하도록 동기화하고, score 와 모델의 가중치를 저장한다.
if done:
agent.update_target_model()
score_avg = 0.9 * score_avg + 0.1 * score if score_avg != 0 else score
print('episode: {:3d} | score avg {:3.2f} | memory length: {:4d} | epsilon: {:.4f}'.format(e, score_avg, len(agent.memory), agent.epsilon))
scores.append(score_avg)
episodes.append(e)
plt.plot(episodes, scores, 'b')
plt.xlabel('episode')
plt.ylabel('average score')
plt.savefig('cartpole_graph.png')
if score_avg > 400:
agent.model.save_weights('./save_model/model', save_format='tf')
sys.exit()
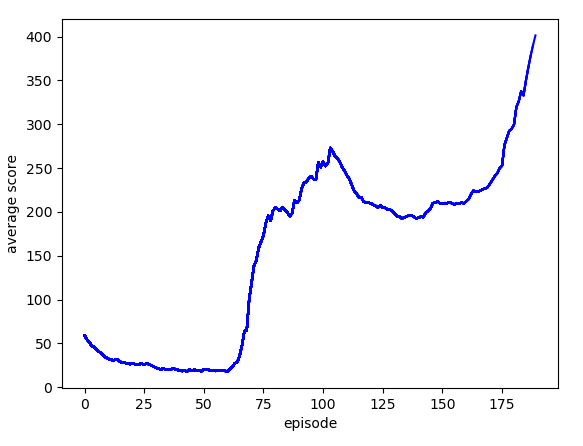
위의 코드는 다음과 같이 실행되어 episode 마다 현재의 상태를 출력한다. episode 가 진행될수록 평균 점수가 높아지는 학습 효과를 확인할 수 있다.
episode: 0 | score avg 59.00 | memory length: 59 | epsilon: 1.0000
episode: 1 | score avg 54.60 | memory length: 74 | epsilon: 1.0000
episode: 2 | score avg 51.44 | memory length: 97 | epsilon: 1.0000
episode: 3 | score avg 47.20 | memory length: 106 | epsilon: 1.0000
episode: 4 | score avg 45.98 | memory length: 141 | epsilon: 1.0000
episode: 5 | score avg 42.88 | memory length: 156 | epsilon: 1.0000
episode: 6 | score avg 40.59 | memory length: 176 | epsilon: 1.0000
episode: 7 | score avg 38.83 | memory length: 199 | epsilon: 1.0000
episode: 8 | score avg 36.05 | memory length: 210 | epsilon: 1.0000
...
episode: 177 | score avg 284.15 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 178 | score avg 292.34 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 179 | score avg 294.70 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 180 | score avg 299.43 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 181 | score avg 319.49 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 182 | score avg 326.04 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 183 | score avg 337.44 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 184 | score avg 332.79 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 185 | score avg 349.51 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 186 | score avg 364.56 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 187 | score avg 378.11 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 188 | score avg 390.30 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
episode: 189 | score avg 401.27 | memory length: 2000 | epsilon: 0.0100
...
cartpole_graph.png 는 학습이 진행되면서 저장된 score의 변화에 대한 그래프를 보여주고 있다.
실행한 결과는 다음과 같이 초반에 불안정하게 막대를 세우는 모습을 보이고 있다.
episode 100회 반복을 넘으면서 안정적으로 막대기를 세우는 모습을 확인할 수 있다.
Reference
모두를 위한 머신러닝과 딥러닝의 강의 - Deep Reinforcement Learning
Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Written on May 5th, 2020 by Jonghyun Ho